Describe The Structure Of An Eye
Ciliary Muscles determines the shape of the Lens. The sclera provides structure and safety for the inner workings of the eye but is also flexible so that the eye can move to seek out objects as necessary.
This black area is actually a hole that takes in light so the eye can focus on the objects in front of it.

Describe the structure of an eye. Conjunctiva - The conjunctiva is a mucus membrane that covers the surface of the eye and the inner part of the eyelids. It is filled with a fluid called the aqueous humor which nourishes the internal structures. Describe the structure of vertebrate eye.
This includes both the Retina and Optic nerve. It is the outer covering a protective tough white layer called the sclera white part of the eye. The anatomy of the eye includes auxiliary structures such as the bony eye socket and extraocular muscles as well as the structures of the eye itself such as the lens and the retina.
It is the clear transparent front part of the eye that covers the iris pupil and anterior chamber and provides most of an eyes optical power if too flat hyperopiafarsightedness. It is known as a lens. This layer is a very stable fibrous membrane that continues to retain the shape of the eye and provides protection.
Its wall is composed of three coats. The human eye is a roughly spherical organ responsible for perceiving visual stimuli. They include the eyebrows eyelids conjunctiva lacrimal apparatus and extrinsic eye muscles figures 97 and 98.
When the muscle contracts the lens is rounder thicker the focal length decreases and more convex and light rays from a near object are sharply focused on the Retina. It consists of the following parts. Anatomically the eye comprises two components fused into one.
The eye consists of three layers of tissue which make up the wall of the eye. The sclera is the outermost layer of tissue also called the white of the eye. Accessory Structures of the Eye.
Depression of the neural groove creates a neural tube. Human eye specialized sense organ in humans that is capable of receiving visual images which are relayed to the brain. The front anterior chamber extends from the cornea to the iris.
Cornea - The cornea is the clear dome-like structure on the front part of the eyeThe cornea delivers 23 of the refracting power to the eye. The eye is a hollow spherical structure measuring about 25 cm in diameter. Structure of Human Eye.
If too steep myopianearsightedness. This allows the eye to take in more or less light depending on how bright it is around you. It has a wall composed of three layers and internal spaces filled with fluids that support the walls and maintain the shape of the eye.
The front transparent part of the sclera is called cornea. The iris controls the size of the pupil which is the opening that allows light to enter the lens. External Layer The external layer of the eye consists of two parts.
The anterior segment is divided into two chambers. The lens is held in position by suspensory ligaments attached to the ciliary body. When the muscle relaxes the Lens is flatter the focal length.
The Cornea is the second structure that light strikes. The iris is the area of the eye that contains the pigment which gives the eye its color. The forebrain of the neural tube develops into primitive structures of the eyeball.
The outermost layer known as the fibrous tunic is composed of the cornea and sclera which provide shape to the eye and support the deeper structuresThe middle layer known as the vascular tunic or uvea consists of the choroid ciliary body pigmented epithelium and iris. A human eye is roughly 23 cm in diameter and is almost a spherical ball filled with some fluid. It needs to be smooth round clear and tough.
The pupil appears as a black dot in the middle of the eye. The lens divides the eye ball into two chambers an anterior aqueous and posterior vitreous chamber. The middle vascular coat choroid ciliary body iris.
The eye contains a transparent biconvex and elastic structure just behind the iris. The outer fibrous coat sclera cornea. It is enclosed within the eye sockets in the skull and is anchored down by muscles within the sockets.
Anatomy of the Eye. Light enters the eye by passing through the transparent cornea and aqueous humor. Cell layers and neural tube development.
The major parts of the eye are shown in figure 915. A camera-type eye contains in the front a light-tight chamber and lens system which focuses an image of the visual field on a light sensitive surface the retina in the back Figure 227. It contains Ciliary Muscles that adjusts the curative of the Lens.
The eye is made up of three coats or layers enclosing various anatomical structures. Eyeball Bulbus oculi The eye is a highly specialized sensory organ located within the bony orbitThe main function of the eye is to detect the visual stimuli photoreception and to convey the gathered information to the brain via the optic nerve CN IIIn the brain the information from the eye is processed and ultimately translated into an image. The ectoderm outer layer is the most relevant in eye development.
Hence it does not possess a perfect spherical shape. The front section anterior segment extends from the inside of the cornea to the front surface of the lens. This area surrounds the pupil and uses the dilator pupillae muscles to widen or close the pupil.
The main parts of the human eye are the cornea iris pupil aqueous humor lens vitreous humor retina and optic nerve. The eye is a hollow spherical organ about 25 cm 1 in in diameter. Embryology of the eye.
All vertebrates possess complex camera eyes. Accessory structures protect lubricate and move the eye. Connected to the sclera are the extra-ocular or extrinsic muscles of the eye.
The sclera and the cornea.
 Eyes Structure Function And Disease The Eyes Are Incredibly Complex Organs In This Article We Explain Their Anatomy How T Eye Anatomy Eyes Treatment
Eyes Structure Function And Disease The Eyes Are Incredibly Complex Organs In This Article We Explain Their Anatomy How T Eye Anatomy Eyes Treatment
 Anatomy Eye Diagram To Label Eye Anatomy Diagram Eye Anatomy Anatomy
Anatomy Eye Diagram To Label Eye Anatomy Diagram Eye Anatomy Anatomy
 Sclera White Of The Eye Medical Anatomy Eye Structure Human Eye Diagram
Sclera White Of The Eye Medical Anatomy Eye Structure Human Eye Diagram
 Cross Section Through The Human Eye Human Body Systems Human Anatomy And Physiology Body Systems
Cross Section Through The Human Eye Human Body Systems Human Anatomy And Physiology Body Systems
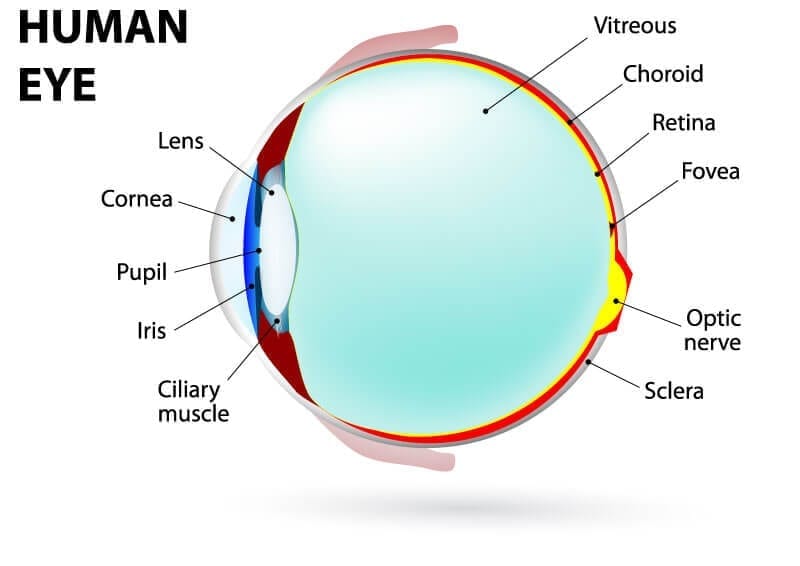 Understanding The Different Parts Of Your Eye All About Eyes
Understanding The Different Parts Of Your Eye All About Eyes
 The Eye And Vision Rectus Muscle Anatomy And Physiology Autonomic Nervous System
The Eye And Vision Rectus Muscle Anatomy And Physiology Autonomic Nervous System
 Module 1 Labeled Diagram Of The Eye Diagram Of The Eye Dot Worksheets Eye Anatomy
Module 1 Labeled Diagram Of The Eye Diagram Of The Eye Dot Worksheets Eye Anatomy
 The Eye Diagram And Functions Functions Of The Human Eye Anatomy Body System Human Eye Diagram Eye Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
The Eye Diagram And Functions Functions Of The Human Eye Anatomy Body System Human Eye Diagram Eye Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
 Structure Of The Human Eye Worksheet Distance Learning Learning Science Distance Learning Life Science Middle School
Structure Of The Human Eye Worksheet Distance Learning Learning Science Distance Learning Life Science Middle School
 Biomedical Devices For The Eyes Lesson Eye Exercises Human Eye Optic Neuritis
Biomedical Devices For The Eyes Lesson Eye Exercises Human Eye Optic Neuritis
 C 2 3 Structure And Function Of The Eye Hsc Biology Eye Function Structure And Function Biology Syllabus
C 2 3 Structure And Function Of The Eye Hsc Biology Eye Function Structure And Function Biology Syllabus
 Label The Parts Of The Eye And Describe How The Eye Works On This Free Printable Workshee Free Homeschool Printables Parts Of The Eye Free Homeschool Resources
Label The Parts Of The Eye And Describe How The Eye Works On This Free Printable Workshee Free Homeschool Printables Parts Of The Eye Free Homeschool Resources
 Anatomy Of The Eye Eye Anatomy Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
Anatomy Of The Eye Eye Anatomy Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
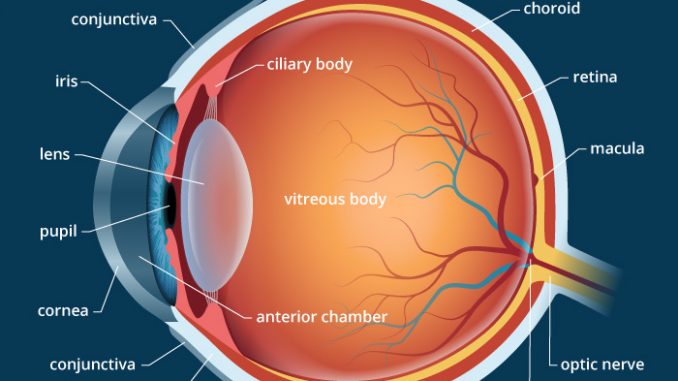 Human Eye Anatomy Parts And Structure Online Biology Notes
Human Eye Anatomy Parts And Structure Online Biology Notes
 Eye Diagram Worksheet Education Com Human Body Science 4th Grade Science Science
Eye Diagram Worksheet Education Com Human Body Science 4th Grade Science Science
 The Structure Of The Eye And The Functions Of These Accessory Structures Eye Structure Ciliary Muscle Eyes
The Structure Of The Eye And The Functions Of These Accessory Structures Eye Structure Ciliary Muscle Eyes
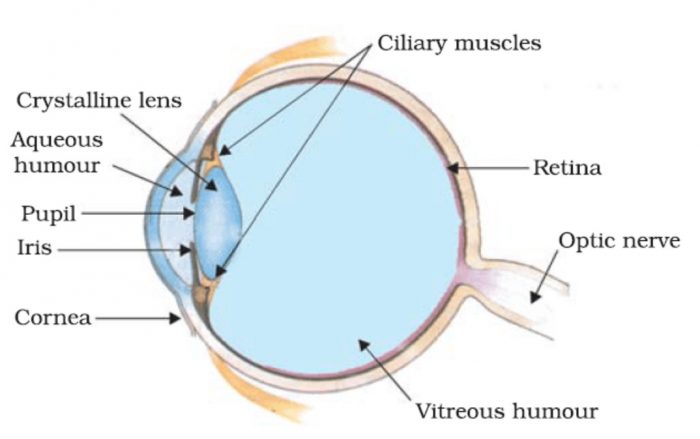 Human Eye Class 10 The Human Eyes And The Colorful World
Human Eye Class 10 The Human Eyes And The Colorful World
 Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Functions Of The Parts Of The Eye Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Parts Of The Eye
Anatomy And Physiology Of The Eye Functions Of The Parts Of The Eye Anatomy And Physiology Physiology Parts Of The Eye


Post a Comment for "Describe The Structure Of An Eye"