Anatomy Of The Eye Vitamin A
It is composed of light sensitive cells known as rods and cones. Layer containing blood vessels that lines the back of the eye and is located between the retina the inner light-sensitive layer and the sclera the outer white eye wall.
 Disorders Of The Eye Poster Eye Disease Anatomical Chart Company Eye Anatomy Eye Health Eye Facts
Disorders Of The Eye Poster Eye Disease Anatomical Chart Company Eye Anatomy Eye Health Eye Facts
Understanding the structure of the eye will help you grasp the role of vitamin A in vision Review the accompanying figure of the eye and the appropriate labels to their respective targets.

Anatomy of the eye vitamin a. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. This single layer of cells helps maintain the function of the photoreceptor cells in the retina by processing vitamin A products turning over used photoreceptor segments absorbing light and transporting nutrients in and out of the photoreceptor cells. The aqueous humour nourishes the lens and cornea and refracts light rays to focus on retina.
Vitamin A plays an important role in your vision. Anatomy of the Eye. It also contains a pigment that absorbs excess light so preventing blurring of vision.
It is a smaller fluid filled chamber between cornea and lens. It is important for growth and development for the maintenance of the immune system and for good vision. Vitamin A has multiple functions.
As with any medication or supplement excessive doses or unnecessary exposure can be harmful. Vitamin A is needed by the retina of the eye in the form of retinal which combines with. Without enough vitamin A your eyes cannot produce enough moisture to keep them properly lubricated.
This is because it is a critical component of the rhodopsin molecule which is activated when light shines on the retina sending a signal to the brain that results in vision. A light sensitive layer that lines the interior of the eye. Sclera - The sclera is the white tough outer covering of globe of the eye.
Your eye also needs vitamin A to nourish other parts of your eye including the cornea. Decomposition of rhodopsin molecules activates an enzyme that initiates a series of reactions altering the permeability of the rod cell membrane. One of the most well-known benefits of vitamin A is its ability to boost vision and keep your eyes healthy.
This vitamin is also a component of rhodopsin a protein in your eyes that allows. The middle layer of the eye between the retina and the sclera. Vitamin A is a precursor of rhodopsin the photopigment found in rods within the retina of our eye that helps us to see at night.
Vitamin A is a group of unsaturated nutritional organic compounds that includes retinol retinal and several provitamin A carotenoids most notably beta-carotene. This article was most recently revised and updated by Kara Rogers Senior Editor. The transparent front window of the eye.
The retinal pigment epithelium is a layer of cells deep in the retina. Vitamin A deficiency which causes reduced photosensitivity of rhodopsin a chromoprotein in rod cells causes night blindness that is usually not severe and vision most often recovers when adequate levels of the vitamin are administered. Cornea - The cornea is the clear dome-like structure on the front part of the eyeThe cornea delivers 23 of the refracting power to the eye.
Vitamin A deficiency stops the production of these pigments leading to night blindness. Conjunctiva - The conjunctiva is a mucus membrane that covers the surface of the eye and the inner part of the eyelids. Without vitamin A night blindness occurs.
The round black hole in the center of the iris. The size of the pupil changes automatically to control the amount of light entering the eye. In the presence of light rhodopsin molecules are broken down into a colorless protein called opsin and a yellowish substance called retinal retinene that is synthesized from vitamin A.
Although the eye is small only about 1 inch in diameter each part plays an important role in allowing people to see the world. Single cell lining absorbs light and prevents scattering phagocytosis of photoreceptor cell fragments stores vitamin A. Vision is by far the most used of the five senses and is one of the primary means that we use to gather information from our surroundings.
A closer look at the parts of the eye By Liz Segre When surveyed about the five senses sight hearing taste smell and touch people consistently report that their eyesight is the mode of perception they value and fear losing most. Eye Anatomy Function and Physiology Facts. The part of the eye that connects the choroid to the iris.
Vitamin A plays a crucial role in vision by maintaining a clear cornea which is the outside covering of your eye. It is a thick nearly circular structure covering the lens. More than 75.
Start studying anatomy chapter 13 the eye and vision. Parts of the eye. VISUAL CYCLE The term visual cycle was coined by George Wald in the mid 1900s to describe the ability of the eye to re-cycle vitamin A for the synthesis of visual pigmentswald1968 As originally proposed Wald1968the rod visual cycle requires the involvement of both retina and the retinal pigment epitheliumRPE in order to properly process the retinal chromophore released from bleached rod pigmentor rhodopsin.
Inner layer of retina transparent composed of photoreceptors. To see the full spectrum of light your eye needs to produce certain pigments for your retina to work properly. The cornea is an important part of the focusing system of the eye.
It is filled with aqueous humour containing aminoacids glucose ascorbic acid hyaluronic acid and respiratory gases.
 What Is The Cornea Human Anatomy Picture Eye Anatomy Eye Anatomy Diagram
What Is The Cornea Human Anatomy Picture Eye Anatomy Eye Anatomy Diagram
 Eye Anatomy Jpg 742 1324 Eye Anatomy Human Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology
Eye Anatomy Jpg 742 1324 Eye Anatomy Human Anatomy Anatomy And Physiology
 Eye External And Internal View Www Anatomynote Com Eye Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye Parts Of The Eye
Eye External And Internal View Www Anatomynote Com Eye Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye Parts Of The Eye
 Urgent Retina Disorders Bonita Springs Jpg 500 320 Pixels Optic Nerve Eye Health Eye Facts
Urgent Retina Disorders Bonita Springs Jpg 500 320 Pixels Optic Nerve Eye Health Eye Facts
 Natural Vision Improvement Pinhole Glasses Http Altered States Net Index2 Php Healing Pinhole Htm Human Eye Diagram Eye Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
Natural Vision Improvement Pinhole Glasses Http Altered States Net Index2 Php Healing Pinhole Htm Human Eye Diagram Eye Anatomy Diagram Of The Eye
 Human Eye Anatomy Cross Section Of The Human Eyeball Viewed From The Side Eye Anatomy Eye Health Eye Care
Human Eye Anatomy Cross Section Of The Human Eyeball Viewed From The Side Eye Anatomy Eye Health Eye Care
 Orbital Bone Anatomy Human Brain Anatomy Anatomy Medical Anatomy
Orbital Bone Anatomy Human Brain Anatomy Anatomy Medical Anatomy
 1 The Human Eye Structure And Function Onmeda De Das Auge Des Menschen Aufbau Und Funktion Onmeda De A Cr Structure And Function Human Eye Eye Structure
1 The Human Eye Structure And Function Onmeda De Das Auge Des Menschen Aufbau Und Funktion Onmeda De A Cr Structure And Function Human Eye Eye Structure
 The Eyes Human Anatomy Diagram Function Definition And Eye Problems Eye Anatomy Eye Health Human Anatomy
The Eyes Human Anatomy Diagram Function Definition And Eye Problems Eye Anatomy Eye Health Human Anatomy
 Vascular Supply Of Eye Anatomy Tendon Of Superior Rectus Muscle Veins Draining Scleral Venous Sinus Eye Anatomy Body Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology
Vascular Supply Of Eye Anatomy Tendon Of Superior Rectus Muscle Veins Draining Scleral Venous Sinus Eye Anatomy Body Anatomy Human Anatomy And Physiology
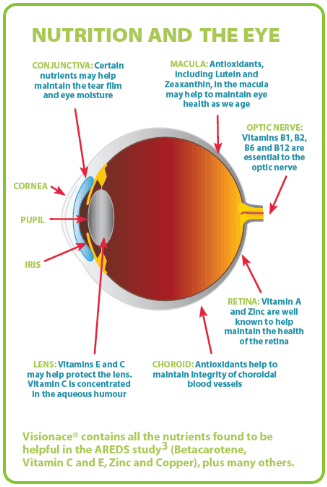 Pin By L Optique Optometry On Interesting Eye Facts Eye Health Eye Care Health Eye Care
Pin By L Optique Optometry On Interesting Eye Facts Eye Health Eye Care Health Eye Care
 Eye Anatomical Chart Eye Anatomy Optometry Infographic Health
Eye Anatomical Chart Eye Anatomy Optometry Infographic Health
 Illustration Showing Parts Of The Inner Eye Retinol Eye Diseases Macular Degeneration Macular Degeneration Symptoms Disease Symptoms
Illustration Showing Parts Of The Inner Eye Retinol Eye Diseases Macular Degeneration Macular Degeneration Symptoms Disease Symptoms
 Hotchsibgrp Wordpress Com I Searched For This On Bing Com Images Eye Anatomy Anatomy Muscle Anatomy
Hotchsibgrp Wordpress Com I Searched For This On Bing Com Images Eye Anatomy Anatomy Muscle Anatomy
 Vitamin A Science Projects All About Eyes Vitamins
Vitamin A Science Projects All About Eyes Vitamins
 Anatomy Of The Eye Tlc Lasik Laser Eye Surgery Healthy Eyes Online Health Store
Anatomy Of The Eye Tlc Lasik Laser Eye Surgery Healthy Eyes Online Health Store
 Eyeball Diagram Cow Eyes Eye Structure Eyeball Diagram
Eyeball Diagram Cow Eyes Eye Structure Eyeball Diagram
 Eyesmart On Twitter Eye Health Eye Anatomy Eyes Problems
Eyesmart On Twitter Eye Health Eye Anatomy Eyes Problems

Post a Comment for "Anatomy Of The Eye Vitamin A"